How to simplify Bitbucket Pipelines configuration management
Bitbucket is a great platform for source control. Its Pipelines was one of the first CI/CD tools built on top of Docker. The obvious integration with other Atlassian tools makes it an ideal tool for a software development company.
So, what's the problem?
Unfortunately, Bitbucket Pipelines is still missing some features that makes it less ideal. In this post I'm focusing on its incapabilities to use projects to configure common Bitbucket Pipelines settings across multiple repositories.
For example, environment variables can be configured either at the workspace or repository level. Projects often have properties which are shared across all their repositories. In a cloud application the AWS region could be one as resources in a single project are usually deployed to the same region. It doesn't make sense to define the region separately on each repository.
On the other hand, a Bitbucket workspace may contain multiple projects which could be deployed to different regions. One reason could be due to the fact that different AWS regions have different services available. Thus workspace level configuration for the AWS region is not a solution either.
Another common characteristics for all repositories in a project is the set of deployment environments. The repositories usually share the same development, test and production environments. Nevertheless they must all be configured individually on each repository.
All this quickly becomes quite complex to manage especially when the number of repositories increases. In the worst case making changes requires modifications to all repositories.
The solution
Using monorepos to reduce the number of repositories is one way to manage the complexity, but doesn't really solve the problem. To address the problems described above, I wrote a simple tool which uses a YAML file to define common properties, and applies them to all repositories in a Bitbucket project.
project:
variables:
AWS_DEFAULT_REGION: eu-north-1
deployments:
dev:
type: Test
variables:
AWS_ROLE_ARN: arn:aws:iam::12345678901:role/bitbucket-pipelines
test:
type: Staging
variables:
AWS_ROLE_ARN: arn:aws:iam::12345678902:role/bitbucket-pipelines
prod:
type: Production
variables:
AWS_ROLE_ARN: arn:aws:iam::12345678903:role/bitbucket-pipelines
The project defines the top-level element. The variables can be used to define project-level environment variables which are applied to all repositories in the project. The deployments defines the deployment environments and their environment variables, if any.
Note: As project.yaml is plain text, you shouldn't use it to store any sensitive information.
When launched the tool iterates through all the repositories in the project and updates them to match the information in the YAML file. Repository variables are updated to match the project-level definitions. Deployment environments and their variables are updated to match the project-level definitions.
By default, the tool does not delete any information even if it's not present in the YAML file are deleted. If you want to make the YAML file the single source of truth, you can configure the tool to delete variables and deployments not present in the YAML file.
Here are the steps you need to do to take advantage of the solution:
- Create a metadata repository in your project. Use
mainas the main branch in the repository. - Insert
project.yamlin the repository to themainbranch. You can copy the template from above. - Insert
bitbucket-pipelines.ymlin the repository with the following content. If you want variables not defined in theproject.yamlto be deleted, you can add--purge-variablesand--purge-secured-variablesto the command-line arguments next to--purge-deploymentswhich deletes deployments that are not included inproject.yaml.
pipelines:
branches:
main:
- step:
name:
services:
- docker
caches:
- docker
script:
- 'docker run -v $PWD:/data
-e BITBUCKET_ACCESS_TOKEN=$BITBUCKET_ACCESS_TOKEN
-e BITBUCKET_WORKSPACE=$BITBUCKET_WORKSPACE
-e BITBUCKET_PROJECT_KEY=$BITBUCKET_PROJECT_KEY
raehalme/bitbucket-project-setup:latest
--purge-deployments
project.yaml'
- In the project settings create an access token with the following access:
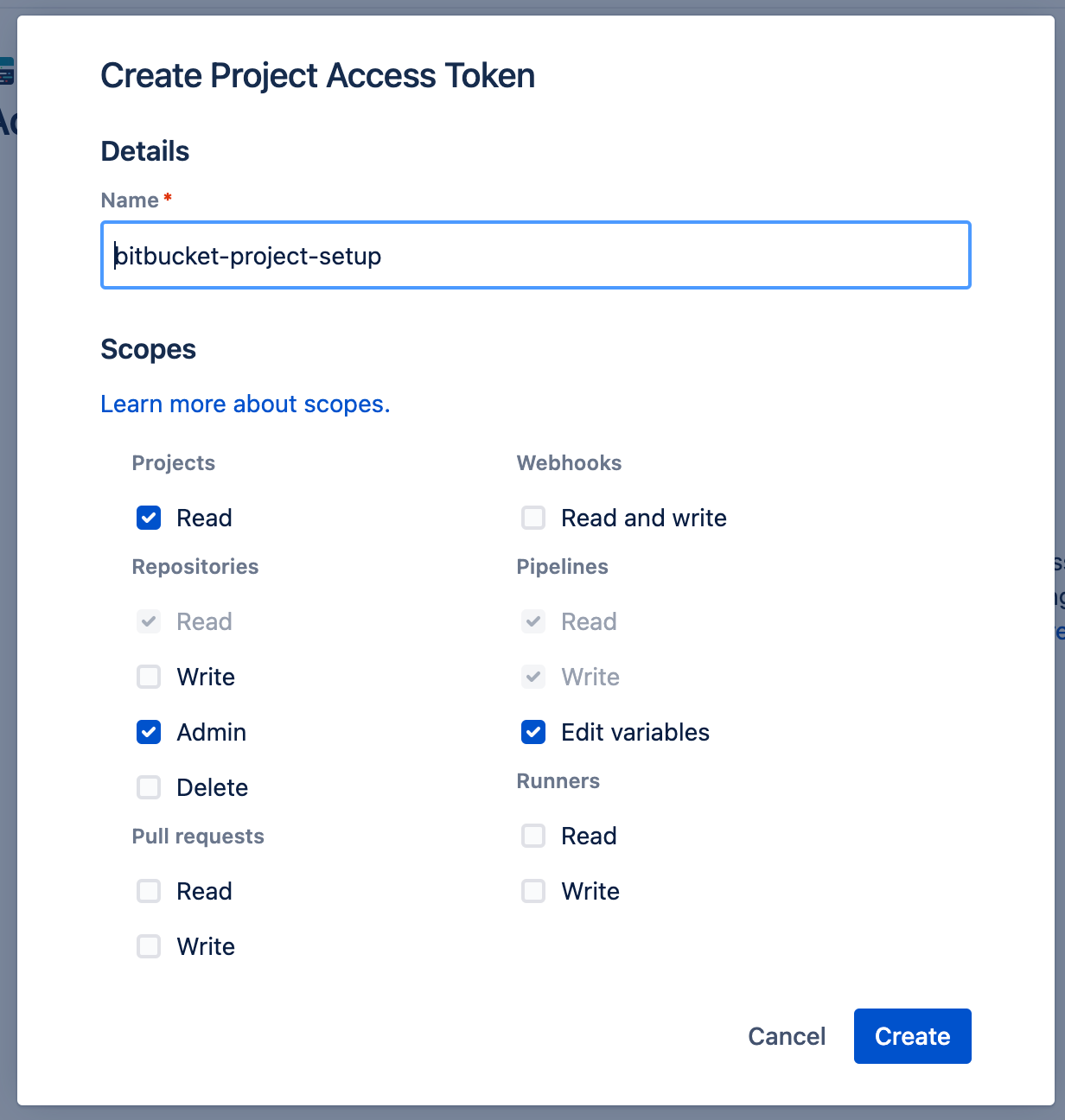
- Define the access token as a repository variable named
BITBUCKET_ACCESS_TOKENin the metadata repository. - Run the pipeline manually to update all repositories with the configuration in
project.yaml.
Source code can be found on Bitbucket under the MIT license. There is also a public Docker image available at Docker Hub, which can be easily used in your Bitbucket Pipelines.